
Quick definition: GSMA SGP.32 is a GSMA-defined eSIM IoT standard that facilitates remote SIM provisioning for IoT devices, enabling them to switch network operators without physical SIM replacement.
Table of contents
- What is GSMA?
- What are SGP standards?
- Bridging the gap: From M2M and consumer eSIM to SGP.32
- The significance of SGP.32 in IoT
- IoT eSIM Architecture – SGP.32
- Impact and applications of GSMA SGP.32 in the IoT ecosystem
- Conclusion: True GSMA SGP.32 is not here yet
What is GSMA?
The GSM Association (GSMA) is an industry consortium representing the interests of mobile network operators globally. Its mission is to unify and drive the collective interests of the mobile ecosystem, particularly in areas like standardization, technology adoption, and rollout of new mobile services.
It is responsible for developing and overseeing standards that ensure compatibility and interoperability across the vast mobile communications network. GSMA’s initiatives and standards, like SGP.32, are instrumental in shaping the future of mobile connectivity and IoT.
What are SGP standards?
SGP standards by GSMA define eSIM technology for seamless device and network interoperability, focusing on security, remote provisioning, and efficiency.
These standards have evolved from their initial M2M roots to address the expanding IoT landscape, which demands connectivity beyond point-to-point to include cloud and data-driven environments.
This evolution led to the creation of standards like SGP.31 and SGP.32, aimed at simplifying remote SIM provisioning for a broad spectrum of IoT use cases, enhancing interoperability and scalability within IoT deployments.
Bridging the gap: From M2M and consumer eSIM to SGP.32
There are two standardized eSIM remote provisioning specifications in use at the moment: Machine-to-Machine eSIM Standard (M2M) and Consumer eSIM Standard.
- M2M eSIM: M2M eSIMs are engineered for IoT devices operating autonomously, without user interfaces. While they fulfill their purpose, several challenges arise. Profile management is cumbersome, often requiring complex back-end integrations for adding or switching profiles. The architecture also necessitates substantial initial investments and leads to situations where devices are locked to specific Subscription Manager Secure Routing (SM-SR) services, restricting flexibility in operator choices.
- Consumer eSIM: Consumer eSIMs, on the other hand, are tailored for devices like smartphones and tablets, relying on user interaction for profile management. This approach, while user-friendly for consumer electronics, is impractical for the vast majority of IoT devices that lack interactive interfaces. The need for device-specific hardware requirements and the absence of scalable profile management further limit their applicability within IoT.
Both standards, while effective within their intended scopes, present significant barriers when applied outside those contexts. M2M eSIMs’ lack of flexibility and consumer eSIMs’ reliance on user interaction highlight the need for a more adaptable solution for the diversity of IoT use cases.
The significance of SGP.32 in IoT
GSMA SGP.32 is the new technical specification for eSIM remote provisioning for IoT devices that face limitations due to poor or unreliable network connectivity or simplified user interfaces.
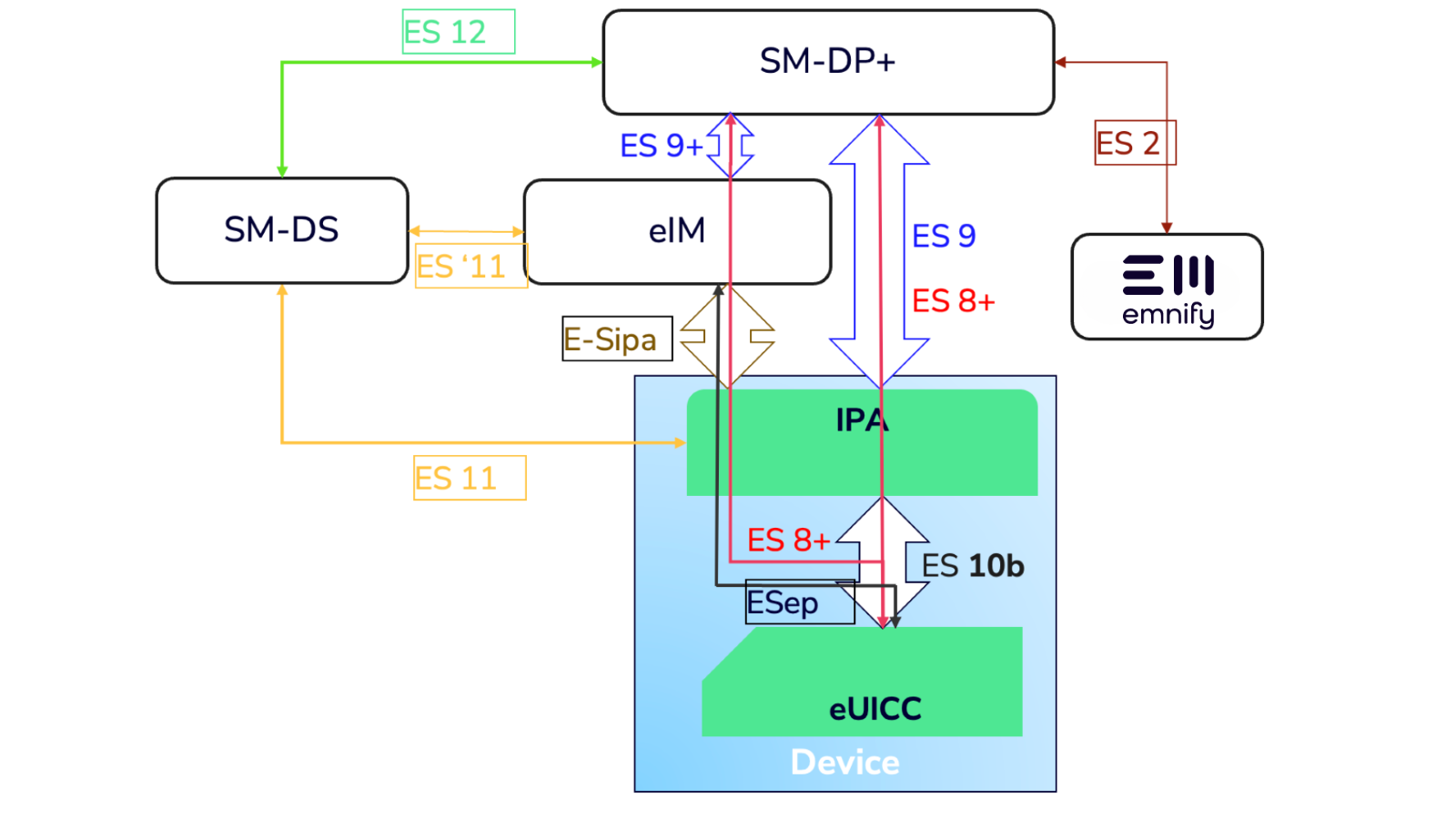
SGP.32 builds on the consumer eSIM model but innovates by splitting the Local Profile Assistant (LPA) into two distinct components: the IoT Profile Assistant (IPA) and the eSIM IoT Remote Manager (eIM).
This architectural change not only simplifies device management but also enhances the capabilities of IoT devices, enabling them to operate more autonomously and efficiently in various network environments.
The eIM's role in eSIM profile management significantly broadens the scope of control across the IoT ecosystem, extending beyond OEMs to include module providers, cloud services, and potentially even Mobile Network Operators (MNOs).
This control extends to managing profile states—such as enabling, disabling, and deleting profiles—remotely, a crucial feature for devices deployed in hard-to-reach or mobile environments.
Furthermore, SGP.32’s approach to device association simplifies the process, making it more accessible for OEMs to implement and manage. For instance, consider an IoT device manufacturer deploying sensors across multiple regions. With SGP.32, they can leverage the eIM for remote profile management and the IoT Profile Assistant (IPA) for seamless profile downloads, eliminating the need for manual SIM changes when devices move between networks.
However, it’s important to note that while SGP.32 has been released, the full implementation and compliance testing for devices and eSIMs are still underway. This means that while the framework is in place, the broader adoption and realization of SGP.32’s full potential within the IoT landscape are anticipated to unfold in 2025.
Impact and applications of GSMA SGP.32 in the IoT ecosystem
By streamlining eSIM remote provisioning, SGP.32 enables IoT devices to be more versatile, scalable, and secure, addressing critical challenges that have previously hindered wide scale IoT adoption.
- Overcoming SM-SR lock-in: A cornerstone of SGP.32’s value is its approach to the SM-SR lock-in challenge prevalent in M2M solutions. By facilitating the association of an eSIM with any eIM throughout its lifecycle and supporting the management of multiple eIMs per eUICC, SGP.32 introduces a new level of flexibility in device management and connectivity strategies.
- Scalability and flexibility: While SGP.32 introduces promising remote management capabilities, its full impact on scalability and operational efficiency, particularly in comparison to existing RSP solutions, remains to be fully realized as it progresses towards widespread implementation. The standard is designed to enhance connectivity flexibility, which could simplify device management in sectors like logistics and transportation. However, the extent to which it will streamline scaling deployments beyond current RSP capabilities is subject to practical application and industry adoption over time.
- Security enhancements: Addressing the concern of security in IoT, SGP.32 establishes robust protocols for eSIM management, including stringent measures for authentication, encryption, and data integrity. This ensures a high level of protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats, instilling confidence in IoT deployments in sensitive areas such as healthcare and financial services.
- Industry transformation: The adoption of SGP.32 is expected to complement and enhance ongoing innovations within various sectors by providing a more streamlined framework for managing IoT devices and connectivity. For instance, in healthcare, where remote patient monitoring is increasingly prevalent, SGP.32-compliant devices could offer improved efficiencies in data transmission and device management, potentially leading to more personalized care. Similarly, in agriculture, where precision farming techniques are already enhancing crop management and yield, SGP.32 could facilitate more seamless integration and management of IoT devices, supporting data-driven decision-making with greater ease.
While the transition to SGP.32 involves a phased approach, the anticipation and preparatory moves by businesses indicate a strong consensus on the standard's potential to overcome previous barriers and unlock new opportunities in IoT.
Conclusion: True GSMA SGP.32 is not here yet
As an active member of the GSMA working group developing the SGP.32 IoT remote provisioning standard, emnify would like to stress that SGP.32 is still in the process of being finalized, with commercial use (potentially) expected to start in 2025. In the meantime, businesses need reliable solutions to navigate their current IoT needs.
The emnify IoT eSIM, designed for global reach and flexibility, supports devices across more than 540 networks in over 180 countries, ensuring seamless operation worldwide. With features like multi-IMSI technology, optimized network selection, and remote management capabilities, emnify’s eSIM is not just compatible with current standards but is also prepared for the next wave of connectivity advancements.
To understand how emnify can support your connectivity needs, we invite you to explore our IoT eSIM Product Guide, offering detailed insights into the features and benefits that make the emnify eSIM an ideal choice for future-proofing your IoT deployments.
Get in touch with our IoT experts
Discover how emnify can help you grow your business and talk to one of our IoT consultants today!

Mario Bucci
With two decades of experience in Italy's premier telecommunications operators, Mario brings a profound understanding of the telco ecosystem to the table. Currently dedicated to innovating within the IoT market, he focuses on developing cloud-native, state-of-the-art communication services on a global scale.


