Quick definition: Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to using network-connected devices and applications to automate, optimize, and manage industrial processes like manufacturing, transportation, and utility management.
Unlike consumer IoT devices, industrial IoT devices are generally used in B2B applications to increase efficiency. And while IoT security is always a concern, it’s crucial in IIoT, where data transmissions often involve sensitive business-critical data.
IIoT links together machine learning, data analytics tools, sensors, and automation that already exist separately in industrial environments. This closer networking of the digital and mechanical worlds creates the potential for profound changes in global industry.
Industrial IoT opens the door to all kinds of improvements in a wide range of industrial-related processes. Companies that rely on the networking of machines and systems will be able to optimize operations, automate production, and improve machine run times. They can drive down ongoing costs with predictive maintenance, servicing machines before they fail.
Imagine you’re operating a large manufacturing plant, and you receive an alert that your cooling tower is consuming far more water than usual. You open an app, and it shows you a spike in water use that just occurred, then suggests the most likely causes, such as an open valve, a leak, or mineral buildup. Then it walks you through troubleshooting steps based on what it knows about your water infrastructure.
Or suppose you manage a fleet of vehicles, and while en route to a job site, the check engine light comes on in one of your trucks. A tracking system connected to the vehicle’s Onboard Diagnostics (OBD) port checks the engine fault code, identifies the exact problem, and notifies you through your fleet management software. Before the driver has even noticed there’s something wrong, your administrator knows whether the vehicle needs to come in for immediate repairs or if you just need to have the shop ready when it returns.
Using low-latency connections, automation, and digitized production, mass manufacturers can have the flexibility to quickly produce new items, achieving on-demand manufacturing.
What is the difference between Industrial IoT and “regular” IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the networking of devices. These devices can communicate independently via networks and perform various tasks. They each have a clear identity and can communicate with one another and receive commands, enabling them to automatically perform tasks without outside intervention.
“IoT” is a broad term for all devices that use networks to enable machine-to-machine communication. It includes industrial applications, but isn’t limited to them. Some of the most common IoT applications include things like vehicle entertainment systems (or even vehicles themselves), wearables, household appliances, consumer electronics, and other everyday devices that collect information about their use, their environment, and their users.
Industrial IoT simply encompasses the industrial applications of IoT technology. Unlike conventional IoT, IIoT doesn’t include consumer products. It focuses on manufacturing, industrial, and smart city applications, typically with a focus on improving processes and reducing costs.
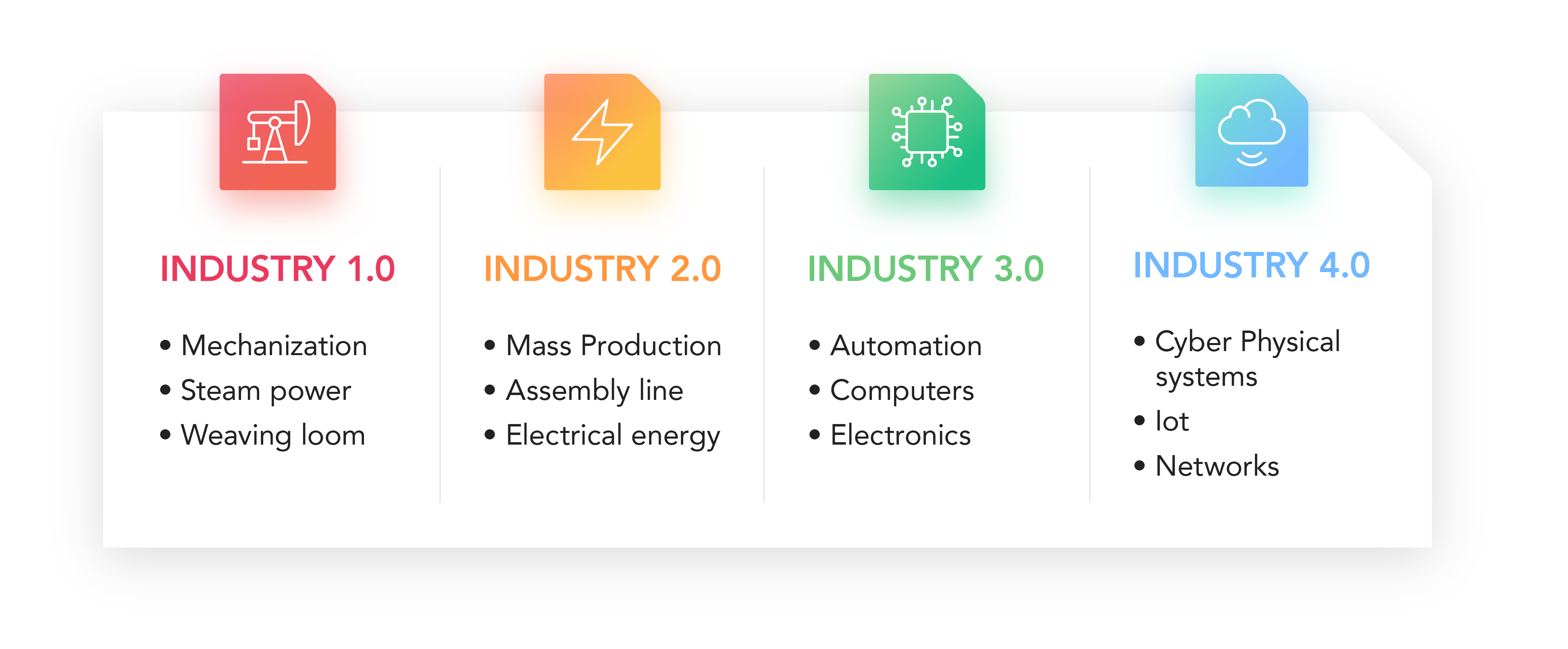
IIoT is highly related to Industry 4.0: the fourth industrial revolution. Industry 4.0 is all about bringing automation and M2M communication to industrial processes, reducing our reliance on human labor and intervention.
The goals of Industrial IoT are to reduce costs in production, improve operational efficiency, ensure faster processes, and enable the implementation of new business models. When used correctly, the Industrial IoT positively impacts a company’s growth, competitiveness, and future viability.
Industrial IoT applications
There are many ways that networking devices can improve a wide range of industrial processes. Two major applications include real-time location tracking and predictive maintenance.
Real-time location tracking
Satellite navigation systems like GPS have had a tremendous impact on everyday life and global business operations. For decades, we’ve been using them to track and locate devices. But satellite navigation systems have two serious disadvantages:
- They only work outdoors
- They’re only accurate within about 10 meters
These properties make satellite navigation systems like GPS limited unsuitable for industrial applications, where precision is crucial and machinery and equipment are typically indoors. Industrial IoT, however, enables businesses to track the positions of products and machinery with pinpoint accuracy and truly real-time tracking.
Using network signals that can penetrate buildings and technology like Real Time Location System (RTLS) sensors, manufacturers and other enterprises can accurately map industrial and logistics processes and analyze and manage them with software. By placing these sensors on boxes within a production facility, for example, the box can automatically trigger sensor activity when moving past various checkpoints, then transmit this activity to software.
IIoT innovations like this will be increasingly important as production processes continue to become more complex, and as manufacturers develop more varied products and smaller batch sizes. Traditional manufacturing makes this difficult to manage, as there’s little transparency in the processing status and manually entering information is highly error-prone.
Accurate product and processing information is vital for maintaining deadlines, keeping quality consistent, utilizing machines efficiently, and compensating for failures. Being able to track products inside and outside of the location enables manufacturers to react to delays, allow for improvements in order planning, and transparently process products.
Predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is already one of the most tangible applications of Industrial IoT. By obtaining status data and analyzing usage metrics from machines, businesses can be more proactive about maintenance, reducing the likelihood of costly unscheduled maintenance and increasing machinery lifespan.
Traditional reactive maintenance is easy to implement but carries a high risk. Even if someone periodically manually inspects equipment and measures crucial metrics, without real-time data, you’re basically waiting for a problem to happen. Reactive maintenance often misses signals that an error or fault is likely to occur, and by not taking preventive measures in time, these failures can result in considerable downtimes.
In practice, predictive maintenance offers a variety of advantages. Knowing the current status of the machine and systems means failures can be avoided and companies can optimize their field service operations. With IIoT, it becomes easier to plan maintenance and service intervals, as well as manage spare parts inventory. In addition, by analyzing the data collected, it is possible to improve machine performance and achieve higher productivity.
Connected future with Industrial IoT
Real-time location tracking, predictive maintenance, data-driven automation, and resource optimization are just a fraction of the possibilities that Industrial IoT offers. In many ways, IIoT is still in its infancy, but manufacturers have recognized the potential of machine-to-machine communication for years. We’re just beginning to see how IIoT and the Industry 4.0 revolution is changing sectors like manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, and utility management.
Whatever your use case, reliable, secure and global cellular connectivity can be a huge differentiator when it comes to your success in Industrial IoT. When all data transmissions can be critical to your business, you can’t afford to lose connectivity.
emnify’s IoT SIM cards and cloud communication platform provide secure, reliable network connections—whether your deployment is indoors, outdoors, underground, or mobile. Every component of our infrastructure is redundant: you can connect to multiple networks, use multiple network infrastructures, and switch between carriers and network services to maximize availability.
Get in touch with our IoT experts
Discover how emnify can help you grow your business and talk to one of our IoT consultants today!
David Garcia
David Garcia brings his passion and over 8 years experience in IoT/IIoT to Product Marketing, along with Extensive experience in Utilities, Energy, Transportation, Manufacturing vertical markets.