
Quick definition: An eSIM is a SIM card that can be updated over the Air remotely.
Traditionally, if you wanted to switch your cellular device's carrier you had to replace the SIM with one from the new carrier. With phones and tablets, this is a simple task. However, for thousands of remotely deployed IoT devices, swapping out SIMs is problematic, especially for devices with embedded SIM form factors that are soldered. In such cases, the SIM is stuck in the device.
The remote SIM provisioning standards were released with the idea to enable SIM manufacturers to create SIMs that could be updated over the air (OTA) and change carriers. These SIMs that can be updated remotely are called eSIM - which led to some confusion because eSIM also refers to a specific embeddable form factor: MFF2. The more distinguished term for the technology that makes remotely switching carriers possible—is embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card (eUICC).
In smartphones, the consumer eUICC has seen huge success under the name eSIM also because the consumer eUICC is already embedded within the device. So the terms eUICC and eSIM are often used synonymously.
The eUICC for IoT devices is called M2M eSIM. And the M2M eSIM does not need to be embedded in the device.
The M2M eSIM provides quite different benefits than the consumer SIM - but the mixup between the two also causes a lot of ambiguity and misconception in the market.
In this article, we’ll explain:
- The difference between a consumer eSIM and an M2M eSIM
- The benefits of using an M2M eSIM
- The difference between an eSIM and multi-IMSI SIM
Let’s start with clarifying the different technologies for consumers and M2M eSIMs.
What’s the difference between a consumer eSIM and an M2M eSIM?
Consumer eSIMs are available in high-end smartphones. The user can select the operator for the eSIM on their phone or by scanning a QR code that directly downloads the new operator profile to the SIM. This “pull” model is quite simple to handle and in fact, there are no to little costs involved.
M2M eSIMs require a different technology because for IoT devices often there is no user, or camera to "pull" the profile to the device. The use case is more about pushing profiles to the device when they are remotely in the field. Therefore M2M eUICCs are registered to an operator-owned remote SIM provisioning platform (RSP) that can then send new profiles to the device. Nevertheless, if the IoT device needs to change operators, migration and integration of the different remote SIM provisioning platforms of the operators are required - which is a project that requires several months and high financial cost.
Further in this post, we will discuss the M2M eSIM for the IoT space.
What are the benefits of a M2M eSIM
There are several key advantages to using a M2M eSIM instead of a conventional SIM. And it’s not just about the higher processing power and RAM of the eSIM itself.
Update the complete SIM Over-the-Air remotely
With the M2M eUICC functionality, the full content of the eSIM can be replaced. The Over-the-Air update is triggered by an SMS - and then the SIM cards check if there is a new profile available on the Remote SIM provisioning platform to be downloaded. Once the profile is downloaded, the old profile can be kept on the eSIM - or also be deleted during the update.
Future Proof for all changes to come
Traditional SIM cards are stuck with the functionality that is available when they are being produced. eSIMs can be updated over the air, with a completely different network coverage configuration, technology, and even applets. Considering the rollout of new radio technologies like NB-IoT, LTE-M, and NB-IoT over Satellite or 5G - an update of the eSIM can enable new technologies to be available for a device when older technologies like 2G or 3G are being shut-down.
Simplified regulatory compliance
Some countries (like Brazil and India) prohibit cellular devices from permanently roaming. In Brazil, for example, you can only roam for 90 days. This means that to be compliant in these countries, you can’t just use a carrier with a roaming agreement with another operator. If you’re going to deploy there, you need to have a SIM that’s associated with a local carrier. With more and more networks adopting regulations - existing SIM cards may not be able to connect to the network in the future.
With an eSIM, you can provision a new SIM profile, so your devices can comply with that country’s telecommunications regulations.
Which form factors are eSIMs available in?
The M2M eSIM is available in all form factors - in standard plastic SIM cards and embedded form factors (MFF2). So pretty much like standard SIM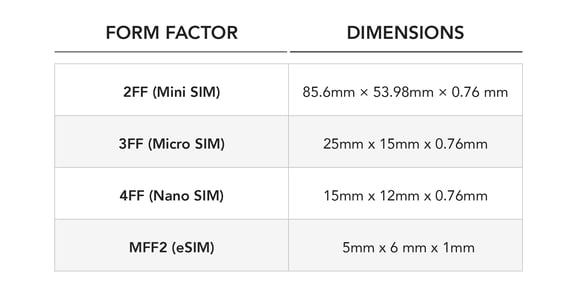
It’s worth noting that a new M2M eSIM form factor type is even smaller. See how the form factors compare to the iSIM.
What's the difference between eSIM and Multi-IMSI?
One of the common myths about M2M eSIM is that with an eSIM profile operators can be easily changed to utilize the better network coverage or pricing of this other operator. See here how we debunk the myth.
The eSIM technology has some drawbacks when thinking about increasing coverage and reducing costs for large data volumes. Namely for M2M eSIMs the profile change to another operator needs to be done manually, and that in case there is no network available for the active eSIM profile then also no new one can be downloaded. Not to mention that after an eSIM profile change, you might end up with a completely different platform with different functionality.
Another option to get better coverage and work with multiple operators is a multi-IMSI applet on the SIM. A multi-IMSI SIM stores multiple International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI). In eSIM terms each IMSI is like a different operator profile that has the network coverage of the operator that IMSI belongs to.
The benefit of the multi-IMSI applet compared to eSIM profile switching is that the SIM automatically switches to the preferred operator IMSI. And in case the multi-IMSI SIM is in an area where the preferred IMSI cannot connect to the available network - the SIM applet switches automatically to a fallback IMSI which can provide access. And overall, even when you change IMSIs and carriers, all your information stays in the same management portal, and also private network functionality stays the same.
Considering an eSIM for your IoT application?
At emnify, we specialize in connectivity for the Internet of Things. Our emnify IoT eSIM combines two technologies - it is an M2M eSIM with a multi-IMSI applet. This ensures that the emnify IoT eSIM can be updated-over-the-Air to futureproof the connectivity even under changing conditions during the device lifetime - but at the same time does not bring any drawback of eSIM profile changes. The emnify IoT eSIM automatically changes IMSIs when they enter different regions or countries to select the best networks and carrier relations. In this way, devices seamlessly select the best network wherever they’re deployed, and you can effortlessly manage your devices from a single, intuitive dashboard.
If you have questions about eSIMs or the best connectivity solution for your business, our team is always happy to help and offer advice. Do you have a use case for the consumer eSIM for devices such as smartphones, tablets, and watches - reach out to also learn about our consumer eSIM offering.
Get in touch with our IoT experts
Discover how emnify can help you grow your business and talk to one of our IoT consultants today!
.jpg)
Jean-Eudes Ambroise
Director of Customer Success at emnify, Jean-Eudes is an expert in IoT.



